In modern industry, especially in the food, medical, and cosmetic packaging sectors, the requirements for material performance are becoming increasingly stringent. High-barrier materials are crucial for ensuring product quality, extending shelf life, and reducing waste. Ethylene-VinylAlcohol Copolymer is seen as a great green packaging material because it blocks gases, smells, and solvents so well. It also possesses good processability, transparency, mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and cold resistance.

EVOH is a type of thermoplastic resin made from ethylene and vinyl alcohol. A key feature is the many hydroxyl groups (-OH) in its structure. These groups create strong hydrogen bonds, which limit how well gas molecules, like oxygen, can pass through it. This gives EVOH very good barrier properties. It blocks oxygen much better than common polymers like polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP). In fact, EVOH can be thousands of times better at blocking oxygen.
1. EVOH EW-3201: Specifications Overview
| Items | Specifications |
| Appearance | White transparent particle |
| Melting index (190℃,2160g/10min) | 1.5-2.5 |
| Chroma | ≤20 |
| Volatile content(%) | ≤0.3 |
| Ethylene(mol%) | 30.0-34.0 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.10-1.20 |
2. In-depth Analysis of Key Physical Properties
2.1 Superior Gas Barrier Performance
The core advantage of EW-3201 lies in its ethylene content, ranging from 30.0 to 34.0 mol%. For EVOH (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxide), ethylene content is a crucial parameter:
- Lower ethylene content: More hydroxyl groups (-OH) on the polymer chain, stronger hydrogen bond network, and better oxygen barrier performance.
- Higher ethylene content: Better polymer thermal processability (melt index, flexibility), and improved water resistance, but slightly reduced barrier performance.
EW-3201's 30.0-34.0 mol% ethylene content provides a good thermal processing window while ensuring extremely high oxygen barrier performance. This method is appropriate for packing food items needing strict preservation (like meats, sauces, and milk products) and medical tools needing high levels of cleanliness, which extends how long they can be stored.
2.2 Ideal Processing Performance
The melt index (MI) of EW-3201 is 1.5-2.5 g/10 min, which is a relatively moderate range.
- Moderate MI: This indicates that its melt viscosity is moderate and its flowability is good, making it suitable for high-speed, complex co-extrusion or lamination processes without excessive degradation during processing.
- Importance in Co-extrusion: EVOH is typically used in thin layers sandwiched between structural layers such as PE, PP, or PET. The MI value helps EW-3201 match well with typical adhesives and outer layers. This makes for good mixing of multilayer structures and strong sticking between layers.
2.3 High Density and High Transparency
EVOH typically has a high density (1.10-1.20 g/cm³), attributed to its highly ordered molecular structure and strong hydrogen bonds. High density is the structural basis for achieving high gas barrier properties. Meanwhile, a colorimetric index below 20 ensures that films or containers made from EW-3201 possess excellent transparency and gloss, crucial performance for packaging that needs to display contents (such as high-end food and cosmetics).
2.4. Environmental Sensitivity
It's important to note that the barrier properties of EVOH are sensitive to environmental humidity. Because the hydroxyl groups on the molecular chain are hydrophilic, when environmental humidity (RH) increases, water molecules enter the hydrogen bond network, weakening hydrogen bonding and leading to increased oxygen permeability.
- Application Solution: EW-3201 is commonly paired with thermoplastics like PE, PP, and PET in real-world uses. This is done through co-extrusion or lamination to create a multilayer structure. The EVOH layer is placed between polyolefin layers that have good moisture resistance. This effectively protects the EVOH layer from moisture, allowing it to maintain excellent barrier performance even in high-humidity environments.
3. Main Applications
- Food Packaging: Used in the production of oxygen barrier films, cling film, aseptic packaging, tubing, and bag-in-bag systems, significantly extending the shelf life of dairy products, jams, meat, seafood, coffee, and tea.
- Medical Supplies: Used for aseptic packaging of infusion bags and medical devices, preventing product oxidation and microbial contamination.
- Industry and Agriculture: Used as an oxygen barrier layer for underfloor heating pipes to prevent pipe corrosion; or for solvent-resistant containers for solvents and chemicals.
- Cosmetic Packaging: Used in the production of multi-layer cosmetic tubing and containers, effectively preventing the oxidation or volatilization of fragrances, vitamins, and other active ingredients.
As the packaging industry needs thinner, more efficient, and greener materials, good ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) products such as EW-3201 (EVASIN EV-4405F) will keep being very important and will push forward barrier packaging tech improvements around the world. Choosing EW-3201 means choosing a high-performance, highly reliable, and sustainable packaging future.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
Since the late 1930s, polyvinyl butyral (PVB), a type of thermoplastic resin, has been key to making laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of one or more layers of PVB film (the interlayer) between two or more pieces of glass, bonded together using heat and pressure. This structure endows the finished glass with a range of unique properties, making it a crucial safety and functional material in the automotive industry and modern construction.
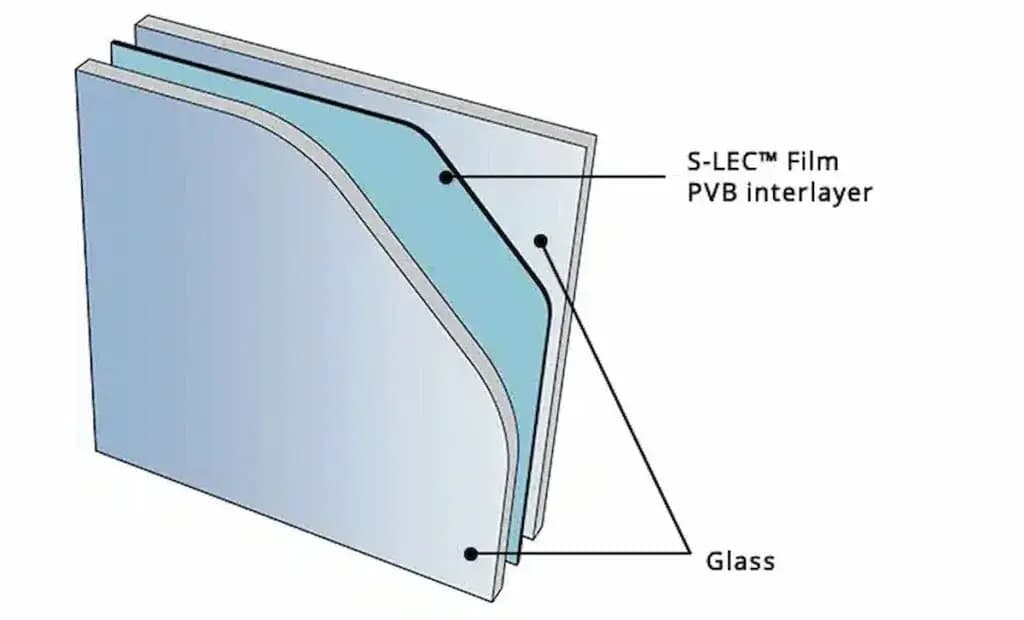
1. Chemical Basis and Unique Properties of PVB Resin
1.1 Structure and Synthesis
PVB resin is a synthetic polymer obtained from polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and butyral through an acetalization reaction. Its molecular chain contains three main functional groups:
- Butyral group: Responsible for providing the polymer with hydrophobicity, elasticity, and solubility.
- Hydroxy group: Maintains the polymer's strong adhesion to glass surfaces, heat resistance, and compatibility with plasticizers.
- Vinyl acetate group:,Usually present in small amounts, it has a fine-tuning effect on the glass transition temperature (Tg) and processing properties of PVB. This unique structure endows PVB with a range of ideal properties for laminated glass applications.
1.2 Key Physical Properties
As the interlayer in laminated glass, PVB film must possess the following core physical properties:
- High Adhesion Strength: Strong adhesion to the glass surface ensures that glass fragments adhere firmly to the film upon impact.
- Excellent Elasticity and Toughness: Ability to absorb impact energy and effectively prevent penetration, forming the physical basis for the safety of laminated glass.
- Optical Transparency: Extremely high light transmittance in the visible light range, without affecting driver visibility or building lighting.
- Aging Resistance: Maintaining its mechanical and optical properties even under harsh environments such as ultraviolet radiation, humidity, and temperature variations.

2. Core Applications and Functions in Automotive Glass
Automotive glass is one of the earliest and most important application markets for PVB resin. PVB plays a dual role in automotive windshields, providing both safety and functionality. CCP PVB B-18FS, combined with plasticizer 3GO and additives, can be extruded to produce various PVB interlayer films for architectural and automotive applications.
2.1 Collision Safety and Fragment Retention
This is the most critical role of PVB in automotive applications. In a vehicle collision, the windshield shatters, but the PVB interlayer can:
- Prevent Penetration: The windshield is designed to take in impact energy. This stops things like stones from getting through the glass into the car. Plus, it keeps passengers inside the car and protects them from head injuries if they hit the glass.
- Fragment Retention: Firmly adhere to broken glass, preventing sharp fragments from flying and causing secondary injuries to passengers.
2.2 Noise Reduction and Sound Insulation Performance
Modern cars need to be more comfortable to drive. PVB films, mostly those made in a specific way, are good at quieting high-frequency vibrations. This cuts down on wind and road noise. For instance, Changchun PVB B-17HX is made with certain plasticizers and a specific molecular weight to improve its damping abilities. It works very well for car side windows and sunroofs, where better sound insulation is needed.
3. Applications of PVB Resin in Architectural Glass
Laminated glass is used in a lot of construction projects. You can find it in curtain walls, skylights, interior walls, and railings. The application of PVB resin must adapt to more stringent requirements for structural strength, durability, and climate change mitigation.
3.1 Structural Safety and Disaster Resistance
The main function of laminated glass in architecture is to provide structural integrity and disaster resistance.
- Storm and Earthquake Resistance: In severe weather, like hurricanes, typhoons, or earthquakes, PVB laminated glass can still hold its structure even if it breaks. This helps keep people and property inside safe, because the glass doesn't collapse or fall apart.
- Theft and Explosion Protection: Thickened multi-layer PVB laminated glass (usually a composite structure of multiple layers of PVB and glass) has extremely high impact resistance. It can effectively resist the impact of blunt objects or gunshots and is widely used in high-security locations such as banks, jewelry stores, and museums. In the shock wave of an explosion, the PVB layer can absorb energy, preventing glass shards from injuring people.
3.2 Energy Saving, Environmental Protection, and Aesthetic Design
Technological advancements in PVB films have also made them part of building energy-saving solutions.
- Solar Control PVB: PVB films containing special additives or dyes can regulate the transmittance and reflectance of sunlight, reducing heat entering the interior (lowering U-value and SC value), thereby reducing air conditioning energy consumption.
- Colors and Patterns: PVB films can be customized in a variety of colors and can even be embedded with patterns or textiles, providing architects with a wealth of facade design and aesthetic choices to meet the complex needs of modern architecture for light, privacy, and appearance.
3.3 Durability and Long-Term Performance
Architectural glass must withstand decades of outdoor exposure. PVB resin possesses excellent durability:
- Aging Resistance: High-quality PVB films have good resistance to ultraviolet rays and moisture, ensuring that laminated glass will not yellow or delaminate during long-term use.
- Edge Sealing: The edge bonding strength between PVB and glass is key to preventing moisture and air penetration, which is essential for maintaining the transparency of laminated glass and preventing internal fogging.
As the automotive and construction industries increasingly demand higher standards of safety, environmental protection, and functionality, PVB resin technology is constantly evolving:
♦ Competition and Integration of Innovative Materials
- While PVB remains the mainstream material, new interlayer materials such as ionic polymers (e.g., SGP/Surlyn) are competing in applications requiring high structural strength and rigidity, particularly in high-rise buildings. The future trend may involve the composite use of PVB with other polymers to achieve a superior performance balance.
♦ Intelligentization and Integration
Future automotive and architectural glass will be more intelligent, with PVB films serving as carriers for functional materials:
- Thermal Management and Electrical Heating: PVB layers can integrate micro-wires or transparent conductive materials for defogging, defrosting, or intelligent dimming of glass.
- Integrated Antennas and Sensors: Integrating vehicle antennas or various environmental sensors into the PVB film layer achieves high functional integration and aesthetic optimization.
♦ Sustainable Development
- Under environmental pressures, developing PVB resins synthesized from renewable resources or bio-based raw materials, and improving PVB recycling technologies, will be significant challenges and development directions for the industry.
Website: www.elephchem.com
Whatsapp: (+)86 13851435272
E-mail: admin@elephchem.com
The Importance of Durable Shoe Soles
In today’s footwear industry, durability, comfort, and performance are key factors that define a brand’s reputation. Whether for professional athletes or everyday users, shoe soles need to withstand long-term wear, provide reliable support, and maintain flexibility. At YY Sole Material, we focus on delivering cutting-edge solutions that meet these demands, helping footwear brands create high-quality products that stand the test of time.

High-Performance Specialty Additive Masterbatches for Superior Polymer Performance
One of the most effective ways to improve shoe sole performance is by using high-performance specialty additive masterbatches. These advanced additive blends are designed to enhance polymer properties during processing, ensuring uniformity and stability in the final product. By integrating these masterbatches into shoe soles, manufacturers can achieve:
- Increased abrasion resistance, reducing wear and tear from daily use
- Enhanced flexibility, improving comfort and cushioning
- Greater compressive strength, supporting stability during high-impact activities
With these benefits, shoes maintain their shape and functionality even after extended periods of use, providing consumers with long-lasting satisfaction.
Wear-Resistant Agent for Sport Shoe Sole: Extending Product Lifespan
For sports footwear, resistance to friction and mechanical wear is critical. Our specially formulated wear-resistant agent for sport shoe sole creates a protective surface layer that reduces degradation caused by running, jumping, and outdoor activities. This agent not only extends the life of the shoe sole but also helps maintain traction and safety, allowing athletes to perform with confidence.
Customization and Technical Support for Optimal Results
YY Sole Material goes beyond supplying materials. We provide fully customized solutions tailored to your production needs, whether for mass manufacturing or small-batch innovative designs. Our technical team works closely with clients to optimize formulations, ensure compatibility with different polymers, and deliver comprehensive support throughout the manufacturing process. This combination of material expertise and service ensures that every shoe produced meets the highest standards of quality and durability.
Partnering with YY Sole Material
Choosing the right materials is essential for creating high-performance, durable footwear. YY Sole Material’s innovative additives and wear-resistant solutions offer a competitive edge, helping brands enhance shoe comfort, durability, and overall user satisfaction.
Discover how our advanced materials can elevate your footwear products by visiting www.yysolematerial.com and exploring our full range of solutions designed to meet the demands of modern shoe manufacturing.
In the footwear industry, material innovation plays a vital role in improving comfort, flexibility, and durability. With the continuous evolution of shoe design and manufacturing, advanced polymer masterbatch technology has become a key factor in achieving superior product performance. At YIYUAN, we are dedicated to developing high-quality masterbatch solutions that enhance both functionality and aesthetics for modern footwear brands.

One of our flagship products, white plastic oil resistant foaming masterbatch pellet, is designed to provide excellent elasticity and oil resistance. It ensures stable foaming performance during injection or compression molding, allowing for lightweight shoe soles without compromising strength. The product also helps maintain color consistency and improves the smoothness of the final surface, making it ideal for sports shoes, casual shoes, and work boots.
We also offer shoe sole masterbatches pellet, specially formulated to improve abrasion resistance, flexibility, and cushioning. These pellets are suitable for EVA, TPR, and rubber-based materials, helping manufacturers produce soles that remain comfortable even after long hours of wear. The masterbatch ensures uniform dispersion in the polymer matrix, enhancing both mechanical properties and visual appearance.
At YIYUAN, every batch of masterbatch pellet undergoes strict quality control and performance testing. Our R&D team continually refines formulations to ensure compatibility with different shoe sole production processes, including injection, extrusion, and foaming. In addition, we provide OEM and ODM customization services, helping global brands create unique and competitive material solutions.
With advanced production equipment, professional technical support, and a strong commitment to sustainability, YIYUAN has become a trusted supplier in the global footwear materials market.
Visit www.yysolematerial.com to learn more about our innovative masterbatch pellets and discover how we can help elevate your shoe manufacturing to the next level.
As industries seek materials that deliver flexibility, durability, sustainability, and cost efficiency, TPEs continue to rise in popularity. At Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing advanced thermoplastic elastomer products engineered to meet diverse and demanding application needs.
This article presents an in-depth look at thermoplastic elastomer uses, their main advantages, and key thermoplastic elastomer applications across major industries.
Before delving deeper into the properties of thermoplastic elastomers, we know that thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are a class of polymers that combine the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elasticity of rubber. They can be melted, molded, and recycled like plastics, while also possessing the feel, resilience, and softness of rubber.
So what are the key characteristics of TPE materials?
- Excellent elasticity and flexibility
- Easy processing via injection molding or extrusion
- Recyclable and environmentally friendly
- Wide hardness range (from very soft to rigid)
- Chemical and weather resistance
- Lightweight and cost-effective
These features enable manufacturers to design products that are both functional and comfortable making TPEs a preferred choice for modern engineering.
Thermoplastic Elastomer Uses in Different Industries
As demand for high-performance materials continues to grow, TPEs have expanded into nearly every industrial sector. Below are some of the most important thermoplastic elastomer uses today.
1.Common applications include:
- Soft grips for toothbrushes, tools, and kitchenware
- Non-slip surfaces for electronics and appliances
- Baby products such as pacifiers and bottle handles
- Protective cases and ergonomic handles
TPEs improve user experience by delivering soft-touch surfaces, cushioning, and anti-slip performance.
2. Automotive Components
TPEs are widely used in the automotive industry due to their durability and ability to withstand harsh environments.
Typical automotive TPE uses include:
- Seals and gaskets
- Interior trims and soft-touch components
- Cable insulation and tubing
- Airbag covers and dashboard parts
Their lightweight nature also contributes to fuel efficiency and vehicle sustainability.
3. Medical and Healthcare Applications
Medical-grade TPEs offer excellent biocompatibility, making them ideal for healthcare environments.
Examples include:
- Medical tubing
- Grips for handheld medical devices
- Seals, plugs, and valves
- Wearable medical equipment
In many cases, TPEs replace PVC or latex to meet modern safety and hypoallergenic requirements.
4. Electronics and Electrical Protection
The electrical and electronics industry benefits from the insulating properties of TPEs.
Applications include:
Cable jackets and connectors
Soft housings for handheld devices
Shock-absorbing protective components
TPEs help improve device durability and ensure user safety.
5. Industrial and Mechanical Uses
In industrial environments, TPEs are valued for their excellent mechanical strength and resistance.
Thermoplastic elastomer uses include:
Seals and O-rings
Vibration-damping components
Wheels, rollers, and grips
Industrial hoses and tubing
Their resistance to fatigue and impact makes them ideal for heavy-duty operations.
Advantages of Using TPE Materials in Manufacturing
Choosing TPEs offers numerous benefits:
✔ Cost-Effective
TPEs require shorter production cycles and reduce material waste, improving manufacturing efficiency.
✔ Environmentally Friendly
They are recyclable and align with global sustainability goals.
✔ Highly Customizable
Hardness, color, elasticity, and performance characteristics can be customized for specific applications.
✔ Excellent Processing Flexibility
Suitable for injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and more.
As a leading manufacturer supplier of thermoplastic elastomer material, Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd. is dedicated to delivering high-quality thermoplastic elastomer products material to meet the evolving needs of global markets. For companies seeking reliable and versatile material solutions, TPEs offer unmatched potential across countless thermoplastic elastomer applications.
When it comes to footwear design, choosing the right sole material is one of the most important decisions for both manufacturers and consumers. TPR TPE Sole Material has gained attention in recent years as brands and factories look for materials that balance durability, comfort, and cost-efficiency. But how do TPR and TPE really compare, and which is better for shoes?
Understanding TPR Sole Material
TPR Sole Material (Thermoplastic Rubber) is widely used in shoe production thanks to its excellent flexibility, slip resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It performs well in casual footwear, children’s shoes, and even certain sports shoes. TPR soles are lightweight and easy to mold, making them a practical choice for large-scale shoe manufacturing. However, they may wear down faster in extreme environments compared to more advanced materials.
Exploring TPE Sole Material
On the other hand, TPE Sole Material (Thermoplastic Elastomer) combines the resilience of rubber with the flexibility of plastic. TPE soles offer superior elasticity, weather resistance, and comfort underfoot, making them ideal for high-performance or premium footwear. Additionally, TPE is often recyclable, which adds to its appeal in today’s eco-conscious market.

Which Is the Better Choice?
The decision between TPR and TPE ultimately depends on your priorities. For affordable, everyday footwear, TPR provides a balance of function and value. For shoes that require greater durability, comfort, or sustainability, TPE is often the better option. Many manufacturers now combine both to optimize performance and reduce production costs.
Why Choose Dongguan Yiyuan TPR TPE Sole Material
For businesses seeking a reliable partner, Dongguan Yiyuan TPR TPE Sole Material offers the perfect solution. With years of expertise in developing both TPR Sole Material and TPE Sole Material, Dongguan Yiyuan delivers high-quality products tailored to your needs. Beyond materials, their commitment to innovation, strict quality control, and excellent customer service ensures long-term value for global footwear brands.
In 2025, choosing Dongguan Yiyuan means choosing both performance and partnership for your shoe business.
Today, era of sustainable innovation, thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) material have become one of the most versatile and eco-friendly materials used across industries. As global manufacturers seek lighter, recyclable, and high-performance alternatives to traditional rubber and PVC, TPE materials stand out as a smarter, greener choice.
What Is TPE Material?
TPE Thermoplastic Elastomer is a unique class of polymer that combines the elasticity of rubber with the easy processing of thermoplastics. Unlike conventional rubber that requires vulcanization, TPE can be molded, remolded, and recycled multiple times while maintaining its original softness and flexibility.
The molecular structure of TPE consists of both hard and soft segments, the hard segments provide strength and stability, while the soft segments ensure elasticity and comfort. This dual structure gives TPE materials exceptional mechanical resilience, flexibility, and environmental adaptability.
Because TPE is 100% recyclable and free from harmful substances such as phthalates, it has become a key eco-friendly elastomer for modern manufacturing.
The Key Differences of TPE vs. Rubber and PVC
When comparing TPE materials with rubber and PVC, several clear advantages emerge:
Recyclability: Unlike rubber, which cannot be remelted after curing, TPE can be recycled and reused without performance loss — making it an ideal sustainable alternative.
Processing Efficiency: TPE can be processed using standard injection molding or extrusion machines, which reduces production time and energy costs.
Safety and Environmental Benefits: TPE is odorless, free of halogens, and compliant with RoHS and REACH standards, whereas PVC may contain chlorine-based compounds.
Design Flexibility: Its broad hardness range (from Shore A 20 to D 50) allows for applications in soft-touch grips, seals, and shoe soles.
In short, TPE is a recyclable and energy-efficient alternative to traditional rubber and PVC, offering improved performance and lower environmental impact.
Main Applications of TPE Materials

Due to its balance of performance, durability, and environmental benefits, TPE has gained wide acceptance across multiple industries:
First and important application is footwear manufacturing:
TPE is increasingly used as an eco-friendly shoe sole material, replacing EVA and PVC for better flexibility, cushioning, and slip resistance.
Automotive Components:
Used for gaskets, seals, and interior trims due to its weather resistance and noise-reduction capabilities.
Consumer Products:
Ideal for soft-touch grips, handles, toothbrushes, and personal-care products where comfort and non-toxicity are important.
Electronics and Cables:
Provides insulation and flexible protection while meeting stringent safety standards.
Medical and Packaging Uses:
With medical-grade formulations, TPE ensures hygiene, biocompatibility, and safety in healthcare and food packaging applications.
These diverse applications demonstrate TPE’s adaptability and reliability as an eco-friendly elastomer suitable for both industrial and consumer needs.
Why TPE Is Considered an Eco-Friendly Material
Sustainability is no longer optional, it is the foundation of modern product design. TPE materials contribute significantly to environmental protection in several ways:
Recyclability:
TPE scraps and end-of-life products can be reprocessed into new materials, minimizing waste.
Energy Efficiency:
Its low processing temperature and absence of vulcanization save energy during production.
Non-Toxic and Safe:
TPE compounds are free from heavy metals, phthalates, and latex — making them safer for both manufacturers and end users.
Long Lifespan:
TPE’s excellent weather, chemical, and UV resistance extend the service life of finished products, reducing replacement frequency.
These advantages make TPE one of the most sustainable and environmentally responsible materials available for industrial and consumer manufacturing.
Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd.: Your Trusted TPE Thermoplastic Elastomer Raw Material Manufacturer
As a professional TPE manufacturer in China, Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd. specializes in developing and producing high-quality, eco-friendly elastomer compounds for global clients. With years of expertise in polymer technology, we provide customized TPE materials tailored to specific applications, from footwear soles to automotive seals.
Our Core Strengths
Custom Formulations: We develop personalized compounds based on hardness, color, and performance requirements.
Strict Quality Control: Every batch undergoes comprehensive physical and chemical testing to ensure consistency.
Sustainability Commitment: Our materials comply with RoHS, REACH, and SGS standards, supporting environmentally responsible manufacturing.
R&D Expertise: Our technical team continuously innovates to enhance product strength, flexibility, and recyclability.
By integrating innovation and sustainability, Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd. helps global partners reduce environmental footprints while maintaining product excellence.
Choosing the Right TPE Grade for Your Application
Different projects demand different material characteristics. Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd. offers a range of TPE grades designed for specific use cases:
Soft-Touch TPE:
Ideal for handles, grips, and over-molding applications.
High-Elasticty TPE:
Used for shoe soles, sports equipment, and seals requiring superior rebound.
Weather-Resistant TPE:
Suitable for outdoor automotive or construction parts.
Transparent TPE:
Commonly used in medical and cosmetic packaging.
Selecting the right compound ensures optimal performance and durability — our engineers can recommend the most suitable thermoplastic elastomer solution for your project.
Building a Sustainable Future with TPE Materials
The global shift toward sustainability demands smarter material choices — and TPE materials are leading this transformation. With their unique combination of flexibility, recyclability, and safety, they are replacing traditional plastics and rubber in countless applications.
At Dongguan Yiyuan Polymer Materials Co., Ltd., we believe that every manufacturer can contribute to a greener planet through responsible material selection. Our mission is to deliver high-performance, eco-friendly elastomers that meet the evolving needs of modern industries.
Explore customized thermoplastic elastomer solutions designed for your sustainable products and global manufacturing goals. Contact today!
Long Carbon Fiber Reinforced PPS
High-performance thermoplastic composites can replace metals. Although PEEK is regarded as the benchmark for engineering performance, reinforced PPS offers a truly cost-effective alternative.
The demand for engineering thermoplastics such as PC and high-performance thermoplastics like PEEK is steadily increasing in industrial applications. These materials, when produced in the form of 3D printing filaments, offer lightweight alternatives to metals for industries such as aerospace and energy.
By incorporating reinforcements, the properties of these high-performance plastics can be further enhanced. For example, the addition of chopped carbon fibers improves both strength and stiffness. Such reinforcements can be applied not only to low- and mid-range engineering plastics but also to high-performance thermoplastics. As long as the 3D printer nozzle can handle abrasive materials, these composites can be printed as easily as standard thermoplastics.
However, a major drawback of high-performance composites such as reinforced PEEK is the high cost of the required 3D printing hardware. These materials demand extremely high extrusion and chamber temperatures, and the equipment capable of meeting these requirements often costs six figures—undermining one of the key advantages of plastic 3D printing: cost efficiency.
This article explores carbon fiber reinforced PPS as an alternative that delivers performance comparable to metals and PEEK, while offering significant advantages in temperature requirements and overall cost.
Introduction to PPS
What is PPS?
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic commonly classified as a high-performance polymer, alongside materials such as PEEK and PEI. It is widely used in machining, mold manufacturing, and additive manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical strength, superior heat resistance compared to standard and engineering thermoplastics, and inherent flame retardancy.
One of the most remarkable properties of PPS is its outstanding chemical resistance. It can withstand a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents, and even shows partial resistance to strong oxidizing agents under certain conditions. However, for particularly aggressive oxidizers such as chlorine dioxide, additional coatings or linings may be required for protection.
With its exceptional performance and more affordable cost compared to PEEK, PPS has found broad applications across various industries. Its mechanical and chemical durability make it ideal for automotive, energy, and chemical processing sectors, while its flame-retardant and self-extinguishing characteristics make it a preferred material for electrical and electronic components, such as surface-mount devices (SMT), motor housings, and transistor encapsulations.
Beyond being an outstanding thermoplastic, PPS is also a reliable replacement for metals such as steel and aluminum. Its thermal stability and chemical resistance enable it to perform effectively in harsh chemical environments, offering strong protection against corrosion and automotive fluids.
PPS as a Composite Material Solution
Reinforced PPS
To improve its strength and rigidity, PPS is often reinforced with chopped carbon fibers or glass fibers, resulting in composite materials with enhanced performance. In fact, PPS is more commonly available in a filled form rather than unfilled.
Researchers have noted that “the addition of carbon fibers significantly enhances the mechanical properties, tribological behavior, post-fire structural integrity, as well as the electrical and thermal conductivity of PPS blends and composites.”

Applications of PPS Composites
- 1. Automotive Industry: High-voltage connectors, battery brackets, motor end covers, and electronic control housings for electric vehicles. Under-the-hood components such as oil pump housings, turbocharger parts, throttle bodies, and cooling system components. Structural components replacing metals, such as seat frames, lamp brackets, and suspension parts.
- 2. Industrial Equipment & Machinery: Precision gears, bearing housings, pump casings, valves, and insulation supports. Industrial jigs, fixtures, tooling bases, and wear-resistant sliding components.
- 3. Electrical & Electronic Components: Motor housings, insulation structures, and high-voltage module casings. SMT trays, electronic packaging carriers, and heat management components.
- 4. Aerospace & Defense: Aircraft structural parts, electronic enclosures, and hydraulic system components.
- 5. Energy & Chemical Processing: Pump bodies, seal rings, flanges, filter housings, and valve components.
- 6. Additive Manufacturing / 3D Printing: Functional prototypes, tooling, fixtures, and low-volume end-use components.
Explore the Future of Lightweight Composites
Discover how Long Carbon Fiber Reinforced PPS can elevate your product performance while reducing weight and cost. Our experienced technical team provides full customization and material support for your project.
Contact Our Team →PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) Material Overview
Introduction
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a linear aromatic high-performance polymer with repeating units of –O–Ph–O–C(=O)–Ph– in its molecular backbone. It is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic and a high-performance specialty engineering plastic with numerous advantages over other specialty plastics.

PEEK has a melting point of 334 °C, a softening point of 168 °C, and a tensile strength of 132–148 MPa. It exhibits excellent mechanical properties, high-temperature resistance up to 260 °C, good self-lubrication, chemical resistance, flame retardancy, peel resistance, wear resistance, and radiation resistance. It can be used in high-end mechanical, nuclear, and aerospace applications. It can also serve as a high-temperature structural material and electrical insulation material, or be compounded with glass fiber or carbon fiber to produce reinforced materials. PEEK is synthesized through a condensation reaction of 4,4′-difluorobenzophenone and hydroquinone in the presence of an alkali metal carbonate, using diphenyl sulfone as a solvent.

Properties of PEEK Resin
PEEK plastic raw materials are aromatic, crystalline thermoplastic polymers with a melting point of 334 °C. They exhibit high mechanical strength, high-temperature resistance, impact resistance, flame retardancy, acid and alkali resistance, hydrolysis resistance, wear resistance, fatigue resistance, radiation resistance, and excellent electrical properties.
High-Temperature Resistance
PEEK resin features a high melting point (334 °C) and a glass transition temperature of 143 °C, with a continuous use temperature of 260 °C. Grades reinforced with 30% glass fiber or carbon fiber have a heat deflection temperature as high as 316 °C.
Mechanical Properties
PEEK resin offers excellent toughness and rigidity. Its fatigue resistance under alternating stress is comparable to that of metal alloys.
Flame Retardancy
Flammability is measured according to UL94 standards, which involves igniting a vertically mounted sample and recording the time taken for it to self-extinguish. PEEK achieves UL94 V-0, the highest flame-retardant rating.
Dimensional Stability
PEEK exhibits outstanding dimensional stability under changing environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity, making it suitable for applications requiring high precision.
PEEK has low injection molding shrinkage, enabling tighter dimensional tolerances than general plastics.
Its low thermal expansion coefficient ensures minimal dimensional changes due to temperature fluctuations.
PEEK maintains stable dimensions under usage and storage, as polymer chain movement is minimal.
Its hydrolysis resistance prevents dimensional changes caused by moisture absorption, unlike common plastics like nylon.
Electrical Insulation
PEEK exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties over a wide temperature range, with low dielectric loss even at high frequencies.
Radiation and Peel Resistance
PEEK resin has good radiation and peel resistance, making it suitable for specialized electrical wires. It can be used in sterilizers and wireless verification systems, providing performance comparable to stainless steel.
Exceptional Performance
- Outstanding high-temperature performance: continuous use up to 250–260 °C, short-term exposure up to 300 °C.
- Very high stiffness, tensile and compressive strength, and impact resistance.
- Excellent flame retardancy: inherent flame retardancy, low smoke and low toxicity.
- Resistant to almost all organic and inorganic chemicals (except highly corrosive agents like fuming sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or dichloromethane).
- High dielectric strength and excellent insulation properties.
- Superior wear resistance and low friction coefficient.
Applications
As a high-performance semi-crystalline aromatic engineering plastic, PEEK can replace metals and ceramics in many demanding applications. Its high temperature resistance, chemical stability, mechanical properties, dimensional stability, low thermal expansion, wear resistance, and self-lubricating properties make it ideal for aerospace, mechanical, petroleum, chemical, nuclear power, and railway industries. Even under 200 °C steam, its tensile strength, mass, and appearance remain stable. It has excellent fatigue resistance under high alternating stress, long-term load-bearing capability, flame retardancy, self-extinguishing property, and environmentally friendly combustion (halogen-free, UL94 V-0, oxygen index 24–35).
PEEK is only soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid and nitric acid; otherwise, it is chemically stable, though insufficiently crystallized PEEK may develop cracks in certain solvents like chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Processing
PEEK can be processed via injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or compression molding. For small-batch or prototype PEEK components, machining from rods or sheets is preferred. Machining should use carbide or diamond tools due to PEEK's wear resistance. Pre-annealing the material can relieve residual stresses, and post-machining stress-relief treatment is recommended to prevent local stress buildup during processing.

Current Uses
PEEK is widely used in electrical insulation (wires, flexible PCBs), mechanical components, chemical equipment, nuclear engineering, oilfield connectors, valves, heat-resistant or corrosion-resistant coatings, and in sterilizers and wireless verification systems, sometimes serving as a stainless steel alternative. Its exceptional combination of properties continues to make it a high-demand material across multiple advanced industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and food processing.

How does a pile of loose ceramic powder transform into a final product with complex shapes and precise structures? All of this is thanks to a key manufacturing step: forming.
Today, we will clearly explain three main ceramic forming methods, exploring their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and typical applications.
1.Dry Pressing
This is the simplest and most common method, very suitable for the mass production of simple-shaped parts.
Working Principle: Ceramic powder mixed with a small amount of binder is filled into a metal mold. Then, high pressure is applied via upper and lower punches to compact the powder into a dense "green body".
Advantages:
High Efficiency: High degree of automation and fast production speed.
Uniform Dimensions: Excellent product consistency.
Low Cost: Suitable for large-scale production.
Disadvantages:
Difficulty in manufacturing complex shapes (e.g., parts with side holes, thin walls).
High mold cost.
Possible uneven density in the green body.
Typical Applications: Ceramic seal rings, gaskets, substrates, bricks, tiles, etc.
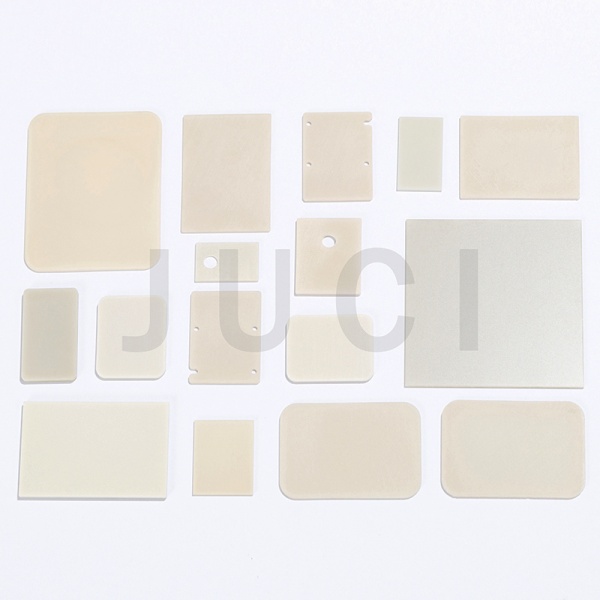

2. Isostatic Pressing
Isostatic pressing was developed to solve the density uniformity issues of dry pressing. It uses a liquid or gas as the pressure-transmitting medium to compress the powder uniformly from all directions.
Working Principle: Ceramic powder is loaded into a flexible rubber or plastic mold, which is sealed and placed into a high-pressure vessel. Pressure is applied via a high-pressure pump, uniformly compacting the powder.
Advantages:
Uniform Density: The properties of the green body are consistent in all directions, which is key for manufacturing high-performance ceramics.
Good Shape Capability: Can produce parts with relatively complex shapes.
Disadvantages:
Large equipment investment.
Production cycle is longer than dry pressing.
Relatively low dimensional accuracy, often requiring subsequent machining.
Typical Applications: Large crucibles, high-voltage electrical insulators, spark plugs, high-performance structural components.
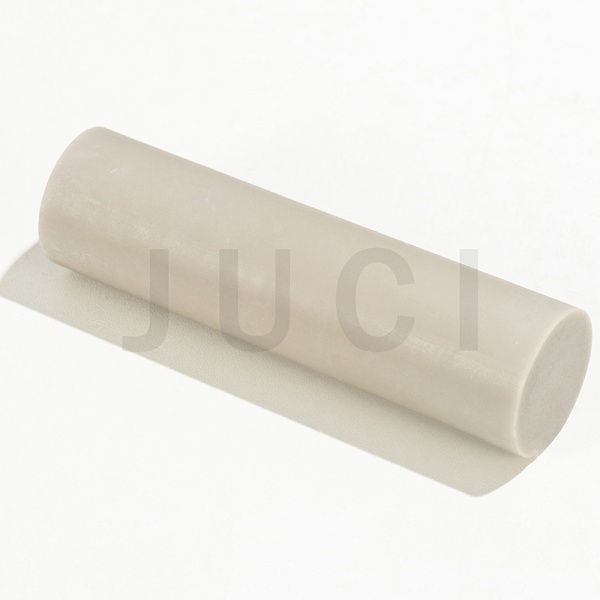

3. Injection Molding
If you need to manufacture ceramic parts with highly complex 3D geometries, similar to metal or plastic parts, injection molding makes this possible.
Working Principle: A large amount of ceramic powder is mixed with a thermoplastic binder and plasticized upon heating. It is then injected into a sealed mold cavity using a screw. After cooling and solidifying, it is demolded to obtain the "green body". Subsequent debinding processes are required to remove the binder before sintering.
Advantages:
Extremely high shape complexity and dimensional accuracy.
Automated production, high efficiency.
Good product consistency.
Disadvantages:
The debinding process is very slow and prone to causing defects.
High cost of molds and equipment.
High raw material cost.
Typical Applications: Micro ceramic gears, engine turbine rotors, medical surgical tools, electronic packaging components, etc.
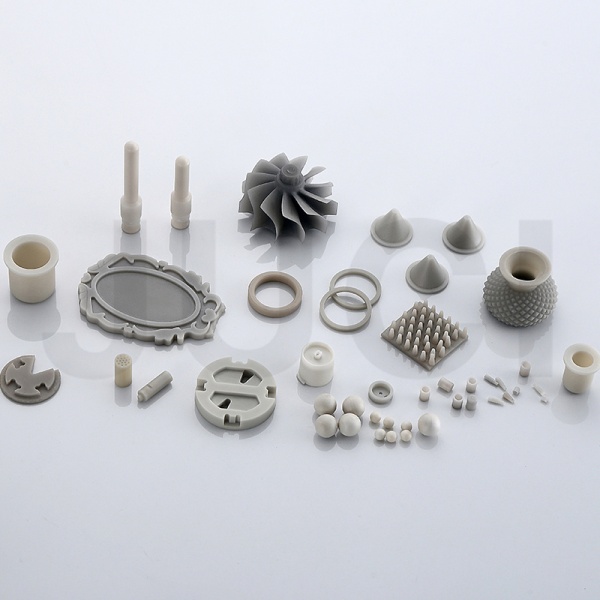

About Xiamen Juci Technology Co., Ltd.
Xiamen Juci Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the research, development, and production of high-performance Aluminum Nitride (AlN) ceramics. Mastering advanced ceramic forming and sintering technologies is crucial for manufacturing its premium AlN products. Aluminum Nitride ceramic is renowned for its high thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, and low thermal expansion.
By leveraging sophisticated processes, including those mentioned above, Juci provides high-quality AlN substrates, structural parts, and heat sinks. These products are vital solutions for thermal management challenges in cutting-edge industries such as 5G communication, new energy vehicles, and high-power LED packaging.
Contact:
Xiamen Juci Technology Co., Ltd.
Phone: +86 592 7080230
Email: miki_huang@chinajuci.com
Website: www.jucialnglobal.com
- Bismaleimide Series2
- Cross-Linking agent / Vulcanizing Agent1
- Curing Agent1
- Engineering Plastic Pellets4
- Epoxy Resin2
- Ethylene-VinylAlcohol Copolymer(EVOH)1
- Fish Oil1
- Food Additives3
- Glucosamine1
- Heat-resistant modifier series1
- High Assay Quaternary Ammonium Compounds9
- Low Assay Quaternary Ammonium Compounds13
- Modified Polyvinyl Alcohol1
- Monomalemide Series2
- Other Surfactants/Catalysts8
- Plastic Random Packing1
- Plastic Structured Packing1
- Polyacrylamide1
- Polyurethane Resin2
- Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)2
- Power Coatings3
- Quaternary Ammonium Hydroxide4
- Special Quaternary Ammonium Compounds7
- TPU4
- Tertiary Amines1
- UV Ink1
- VAE Emulsion (Vinyl Acetate–ethylene Copolymer Emulsion)1
- aluminum paste1
- antiform2
- fire sleeve2
- resin2